Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- Understanding Snowflake Security Architecture
- Best Practices for Snowflake Security
3.1 Secure Network Connectivity
3.2 Data Encryption
3.3 Access Controls and Privilege Management
3.4 Audit Logging and Monitoring - Snowflake HIPAA Compliance
4.1 Data Protection
4.2 Access Controls
4.3 Audit and Risk Management - Snowflake Secure Data Sharing
- Conclusion
Introduction:
As organizations leverage Snowflake for data storage and processing, adhering to best practices in security and compliance becomes essential. This guide explores Snowflake’s security best practices, including HIPAA compliance measures, and strategies for secure data sharing. By implementing these practices, organizations can safeguard their data while meeting regulatory requirements.
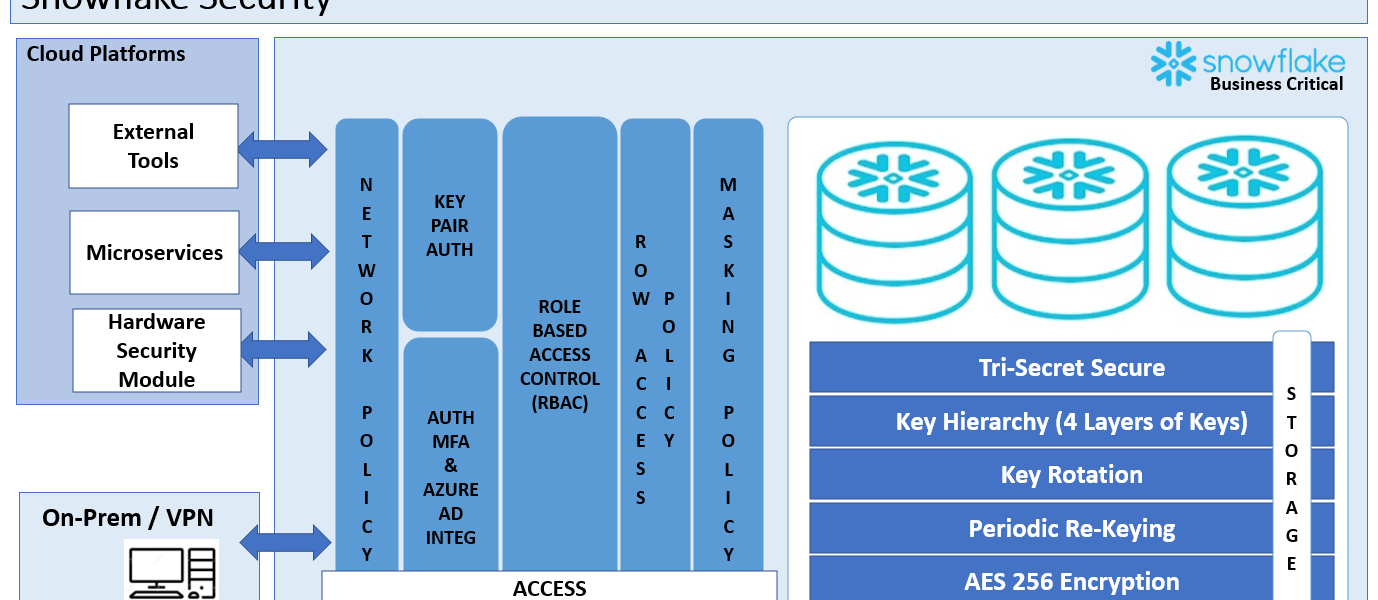
Understanding Snowflake Security Architecture:
Snowflake employs robust security measures, including network security, data encryption, and access controls, to protect data at rest and in transit. These measures are crucial for maintaining compliance with regulations like HIPAA.
Best Practices for Snowflake Security:
- Secure Network Connectivity:
- Utilize Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) peering or PrivateLink for private network connections to Snowflake.
- Implement IP whitelisting to restrict access and enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for enhanced security.
- Data Encryption:
- Employ Snowflake’s encryption capabilities to encrypt data at rest and in transit.
- Utilize client-side encryption for end-to-end data encryption before uploading data to Snowflake.
- Access Controls and Privilege Management:
- Implement role-based access control (RBAC) to enforce least privilege access policies.
- Utilize hierarchical access control (HAC) for granular access management.
- Audit Logging and Monitoring:
- Enable comprehensive audit logging and integrate with SIEM tools for real-time monitoring.
- Regularly review audit logs to detect and respond to security incidents.
Snowflake HIPAA Compliance:
- Data Protection:
- Encrypt data and implement access controls to protect electronic protected health information (ePHI).
- Implement data anonymization and pseudonymization techniques to ensure data privacy.
- Access Controls:
- Enforce stringent access controls to restrict access to ePHI based on user roles and permissions.
- Regularly review and update access controls to maintain compliance with HIPAA requirements.
- Audit and Risk Management:
- Conduct regular risk assessments and audits to identify and address security vulnerabilities.
- Ensure compliance with HIPAA’s requirements for data access, transmission, and storage.
Snowflake Secure Data Sharing:
- Secure Data Sharing:
- Leverage Snowflake’s secure data sharing capabilities to share data with trusted partners securely.
- Implement encryption and access controls to protect shared data and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Conclusion:
By implementing Snowflake’s security best practices and adhering to HIPAA compliance measures, organizations can ensure the secure storage, processing, and sharing of data. With robust security measures in place, organizations can leverage Snowflake’s capabilities for secure data sharing while maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements.